Rice Blast Disease – A Threat to Rice Crops
Blaze Disease – A Threat to Rice Plants
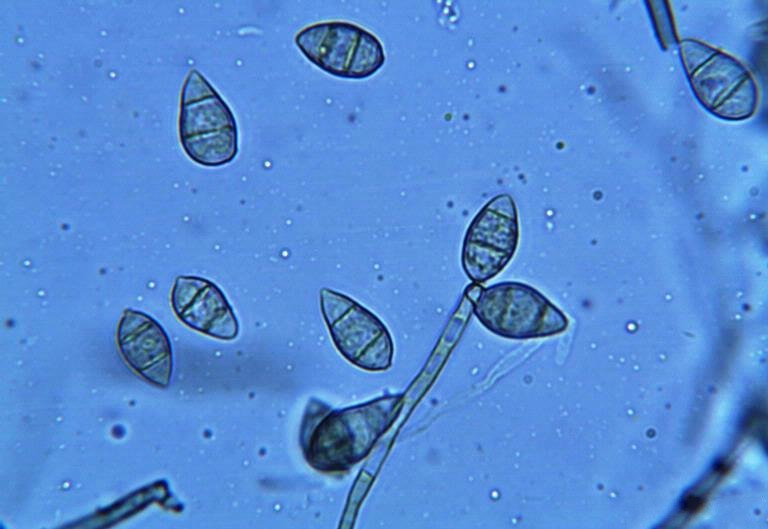
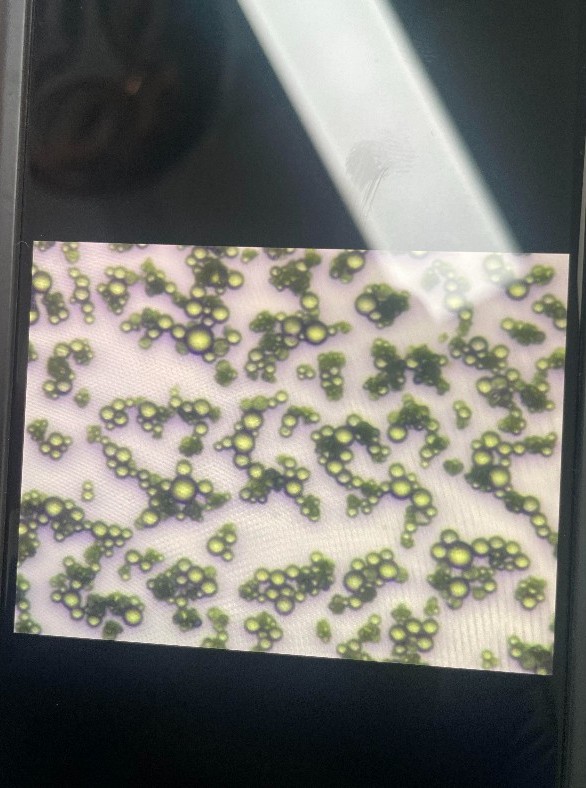
(Magnaporthe oryzae)
1. Introduction to rice blast disease

Blaze disease (Magnaporthe oryzae) is one of the most common and dangerous diseases of rice. This disease causes serious damage to crops, especially in rice growing areas around the world, including Vietnam. Rice blast disease not only reduces rice yield but also affects rice quality, causing great economic losses to farmers.
The origin of rice blast disease is the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. This fungus can attack different parts of the rice plant, such as leaves, stems, panicles and grains, making the plant weak and susceptible to other agents.
2. Symptoms of rice blast disease
Blaze disease usually appears mainly on the leaves, then can spread to the stems and panicles of rice. The main symptoms include:
On the leaves: The disease initially appears as small, round, gray-green spots that gradually enlarge and become diamond-shaped. The lesions usually have a gray or white center and a brown or black border. When the lesions become large, the rice leaves dry out and die early, resulting in the plant being unable to photosynthesize effectively.
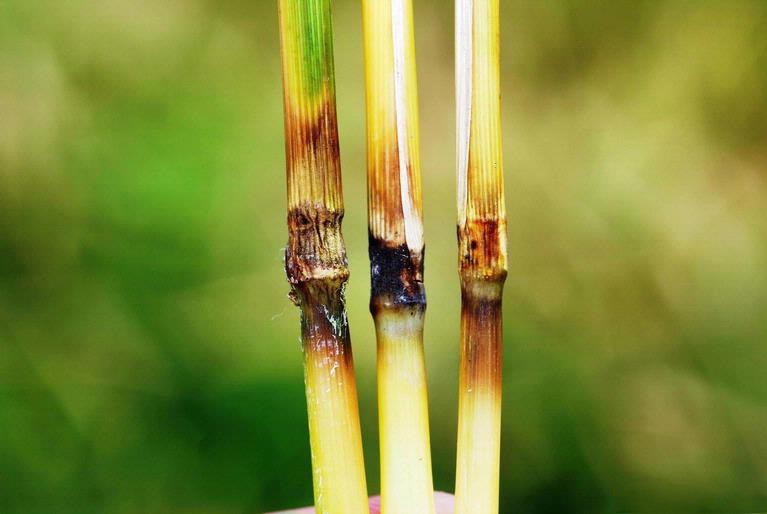
On the rice neck: When the fungus attacks the rice neck (the base of the rice panicle), the lesions appear brown or black, causing the panicle neck to wilt. The diseased rice panicle will not be able to bloom evenly and the grains will be flat or rotten.
On the stem: Similar to the leaves, the lesions on the stem are diamond-shaped with a gray center and a brown-black border. The diseased rice stalk will be weak and prone to breakage.
On the grain: When blast disease attacks rice grains, it causes the grains to not develop fully, reducing the quality of the rice, causing direct damage to the yield.
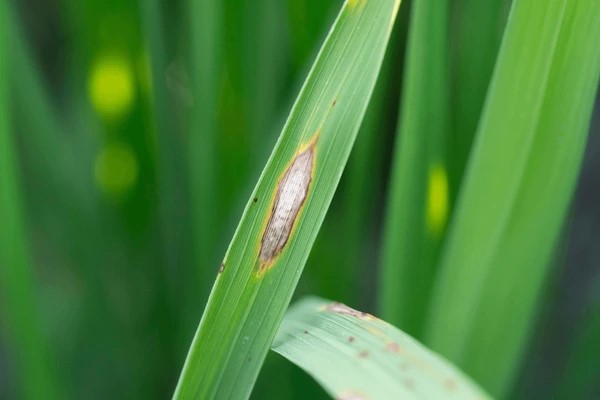

3. Causes and conditions for the occurrence of rice blast disease
Blaze disease is mainly caused by the fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. This fungus thrives in hot and humid weather conditions, especially during the rainy season or in places with high humidity and temperatures ranging from 25-30°C. Some factors that increase the risk of disease outbreak include:
Weather conditions: Humid weather and warm temperatures are favorable environments for fungus growth. Night dew and continuous rain over long periods of time also create conditions for the disease to spread.
Sensitive rice varieties: Some rice varieties are not resistant to the disease and are more susceptible to blast than others. Using sensitive rice varieties in adverse weather conditions can cause disease outbreaks.
Inappropriate fertilization: Excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers causes rice plants to grow quickly but weakly, creating favorable conditions for fungus to attack. In addition, unbalanced fertilization (lack of potassium and phosphorus) is also a factor that contributes to increased risk of disease.
High planting density: When rice plants are planted too densely, air circulation between plants is difficult, creating a humid environment that is prone to disease.
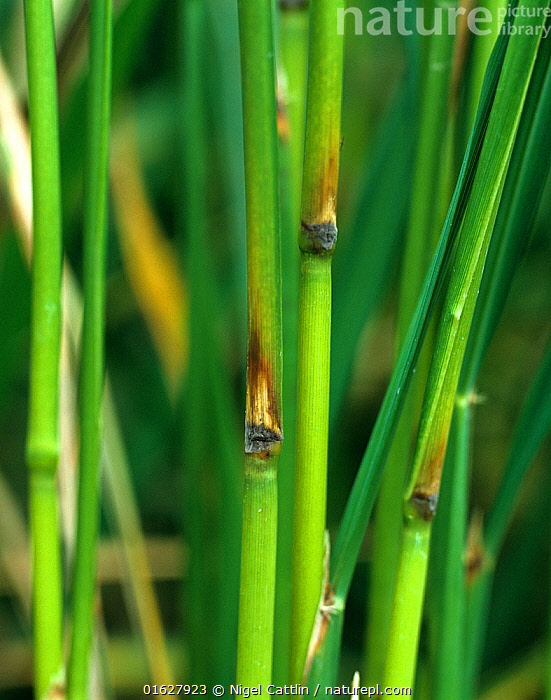

4. Harmful effects of blast disease
Blaze disease causes serious damage to the rice industry, especially in years with unfavorable weather. The harmful effects of the disease are not only limited to reduced productivity but also affect the quality of rice grains. Some of the main harmful effects include:
Reduced productivity: Blast disease causes rice leaves to wither, reduces the ability to photosynthesize and makes the plant weak and unable to grow strongly. When the disease attacks the panicle, the rice grains cannot ripen evenly and are prone to being empty.
Reduced rice quality: Diseased rice grains will be empty or rotten, leading to poor quality rice that is difficult to sell on the market.
Economic damage: Blast disease is one of the main causes of crop failure in many areas, causing farmers to suffer great economic losses. Not only is rice income lost, but the cost of disease treatment also increases, reducing farmers' profits.
5. Measures to prevent and control rice blast
Controlling rice blast requires a combination of farming practices, using disease-resistant varieties, and applying pesticides. Here are some effective measures to help prevent rice blast:

5.1. Using disease-resistant varieties
One of the most effective measures to reduce the risk of rice blast is to use disease-resistant rice varieties. Currently, agricultural research institutes have developed many rice varieties that are resistant to rice blast, helping farmers minimize damage without relying too much on chemicals.
5.2. Proper fertilizer management
Nitrogen fertilizer plays an important role in the development of rice plants, but applying too much nitrogen will make the plants susceptible to disease. Farmers need to balance nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus, and limit nitrogen fertilization when the rice plant is in a stage sensitive to disease, such as when it has just been planted or before flowering.
5.3. Adjusting planting density
Planting density that is too high creates conditions for fungal diseases to develop. Therefore, farmers need to plant rice at a reasonable distance, helping the rice plant have enough space to grow and better air circulation.
5.4. Using pesticides
In cases where rice blast disease has appeared in the field, using pesticides is a necessary measure to prevent the spread of the disease. However, the use of pesticides must comply with the "4 rights" principle (right drug, right dosage, right time and right way) to achieve high efficiency and limit harm to the environment.
Some recommendations for
pesticides containing Tricyclazole, Isoprothiolane, Azoxystrobin disease-fighting ingredients, good for crops such as: Downy 650WP, Trinong 50WP, Afenzole 325SC Top
5.5. Cultivation measures
Farmers need to implement disease-free cultivation measures such as plowing, drying fields to destroy pathogens from the previous crop. At the same time, crop rotation (planting rice with other crops) is also an effective way to reduce disease pressure in the fields.
6. Conclusion
Blaze disease is a major threat to rice yield and quality worldwide, especially in hot and humid climates like Vietnam. Understanding the causes, symptoms and disease prevention measures is essential for farmers to respond promptly and minimize damage caused by the disease. The combination of using disease-resistant varieties, proper fertilizer management and applying proper cultivation measures will help effectively control blast disease, contributing to improving productivity and income for farmers
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



