Powdery Mildew – Causes, Symptoms and Prevention
Powdery Mildew – Causes, Symptoms and Prevention
1. Introduction to powdery mildew
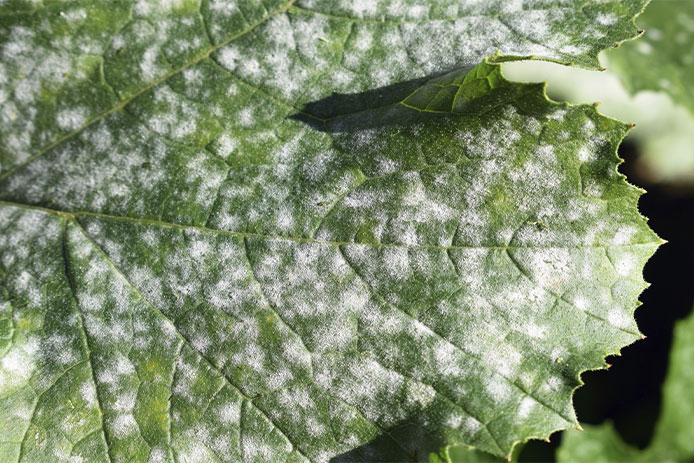
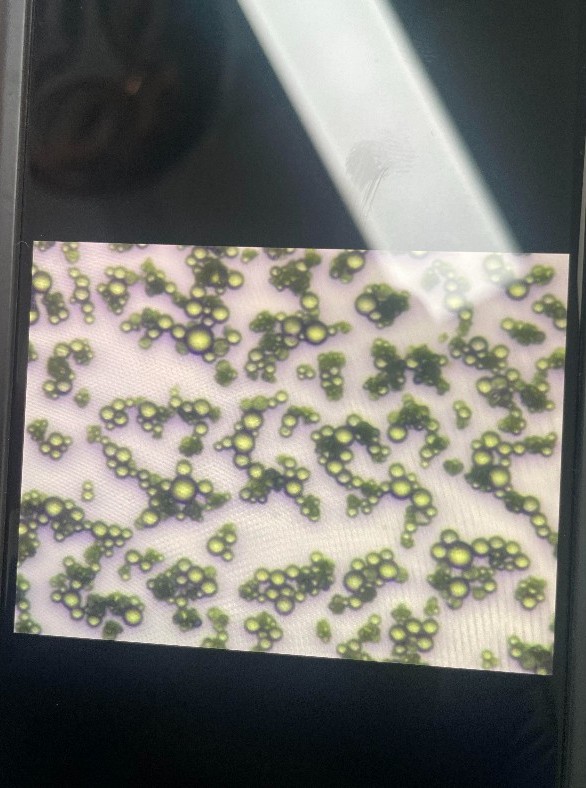
Powdery mildew is one of the most common plant diseases, seriously affecting the growth and productivity of many different crops, including vegetables, crops, fruit trees, and industrial crops. . The disease is caused by a group of fungi belonging to the genera Erysiphe and Oidium, with the easily recognizable characteristic of a white powdery layer appearing on the surface of leaves, stems or fruits of plants.
Powdery mildew not only causes reduced productivity but also reduces the quality of agricultural products, causing great economic loss to farmers and producers. Understanding the causes and prevention of powdery mildew is very important to protect plants from the effects of the disease.
2. Symptoms of powdery mildew
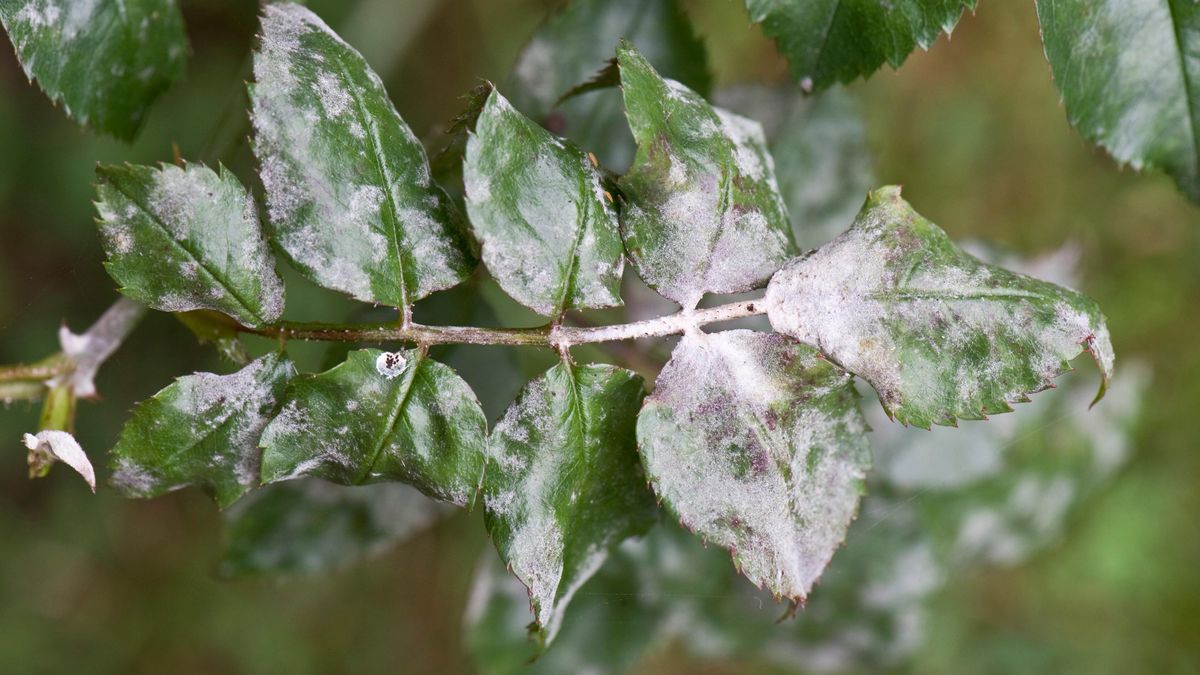

Typical symptoms of powdery mildew are easily recognizable through the following signs
- On leaves: Initially, tiny white powdery spots appear on the leaf surface, usually on the underside of the leaf, then gradually spread to the entire leaf. These white powdery spots form a thin layer of powder, which looks like chalk dust. When the disease is severe, the leaves will turn yellow, wilt and fall prematurely, reducing the plant's ability to photosynthesize
- On trunks and branches: Fungal diseases can also attack tree trunks and branches, creating white powdery spots, causing the tree to grow weakly, be susceptible to breakage and overall weakness.
- On fruit: Powdery mildew can appear on the surface of young fruit, affecting fruit development. Diseased fruits often do not develop normally, are distorted, cracked, and reduce commercial quality.
Powdery mildew symptoms often appear best in spring or early summer, when the weather is warm and humid. The disease can spread quickly, especially in weather conditions that are favorable for the growth of pathogenic fungi.
3. Causes and conditions of powdery mildew disease

Powdery mildew is caused by many species of fungi, the most common being Erysiphe, Oidium, and Sphaerotheca. These fungi thrive in warm, humid, and windy conditions. Some key factors that increase the risk of powdery mildew outbreaks include:
- Weather conditions: Powdery mildew thrives in temperatures ranging from 15-25°C, high air humidity and fog or drizzle. Weather that is cool at night and dry during the day also creates ideal conditions for fungus to grow.
- High density of plants: When plants are planted at too high a density, air does not circulate well, creating conditions for fungi to grow and spread. Plants grown close together are more susceptible to disease than plants grown in well-ventilated areas.
- Sensitive plant varieties: Some plant varieties have weak disease resistance and are easily attacked by powdery mildew, especially plant varieties with thick, succulent leaves.
- Improper plant care: Nutrient deficiencies, especially potassium and calcium, also make plants weaker and more susceptible to disease. Unbalanced fertilization and using too much nitrogen fertilizer also contribute to increasing the risk of disease.
4. Harmful effects of powdery mildew
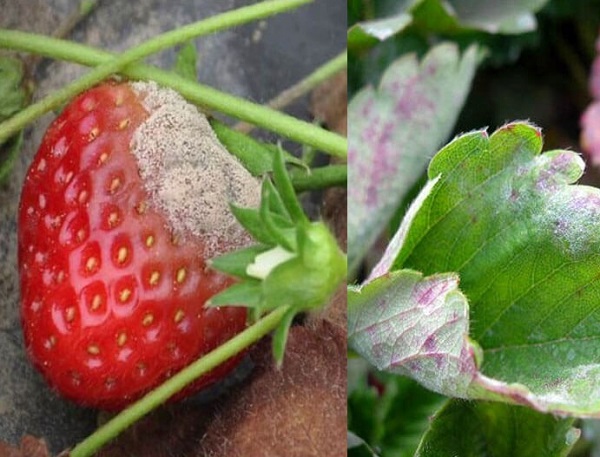

Powdery mildew can cause many serious harms to plants and agriculture, including:
- Reduced yield: When plants suffer from powdery mildew, the photosynthetic ability of leaves is severely reduced, leading to the weakening of the entire plant. Plants cannot grow strongly and produce lower yields than normal.
- Reduced quality of agricultural products: Fruits infected with powdery mildew are often small, distorted, not of commercial quality, and have reduced economic value when sold on the market.
- Increased production costs: To control powdery mildew, farmers have to spend a lot of money on pesticides and crop care measures, increasing production costs.
- Economic damage: Powdery mildew, if not controlled promptly, can cause crop failure and great losses for farmers and manufacturers, affecting income sources and food security.
5. Measures to prevent powdery mildew
Controlling powdery mildew requires a combination of cultural practices, pesticide use and proper nutrient management. Here are some effective prevention measures:

5.1. Use disease-resistant varieties
Using plant varieties with good disease resistance is one of the most important measures to prevent powdery mildew. Agricultural research institutes have been developing many crop varieties that are resistant to this disease, helping to minimize the negative effects of the disease.
5.2. Manage growing conditions
- Reasonable planting density: Plants should be planted at a reasonable distance to create ventilation conditions, help air circulate better and limit the growth of disease-causing fungi.
- Water properly: Limit watering too much in the evening to avoid plants becoming too wet, creating a favorable environment for fungus to grow. Watering early in the morning will help the plant dry faster.
5.3. Nutritional management
Providing adequate and balanced nutrition for plants is an important measure to help plants grow healthily and increase their resistance to diseases. In particular, it is necessary to fully fertilize potassium and calcium, two important elements that help strengthen the plant's resistance.
5.4. Use pesticides
In cases where powdery mildew has appeared on the plant, it is necessary to use pesticides to control the growth of the fungus. Sulfur-based, copper-based or biological fungicides are often used effectively in controlling powdery mildew. However, it is necessary to comply with the "4 rights" principle (right drug, right dose, right time, and right way) to achieve high efficiency and limit impact on the environment.
Some types contain the ingredients Sulfur, Tebuconazole such as: BACCA 80WG, Gone Super 350EC can effectively treat powdery mildew on plants, and is environmentally friendly
5.5. Farming measures
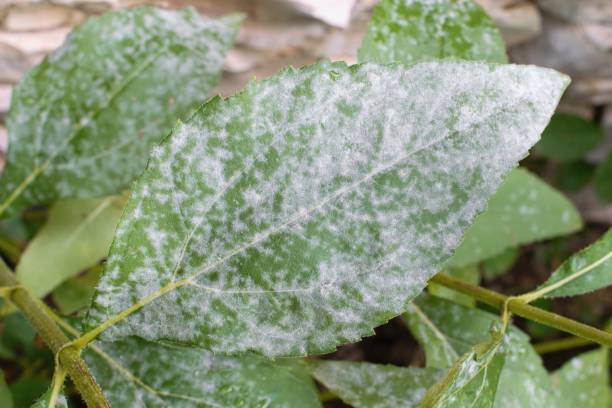

- Crop rotation: Rotating crops between crops helps limit the accumulation of disease-causing fungi on soil and plants.
- Field cleaning: It is necessary to regularly clean, collect and destroy diseased plant parts to prevent the spread of the disease. After harvesting, the soil should be plowed and dried to destroy remaining pathogens.
6. Conclusion
Powdery mildew is one of the most common and dangerous diseases for many plants. The presence of the disease causes great damage to productivity and quality of agricultural products, while also increasing production costs for farmers. However, with reasonable prevention and management measures, farmers can completely control powdery mildew, protect crops and improve production efficiency.
The combination of using disease-resistant varieties, good management of nutrients and the growing environment, along with applying proper plant protection measures, will help minimize damage caused by powdery mildew and protect resources. economic benefits for growers.
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



