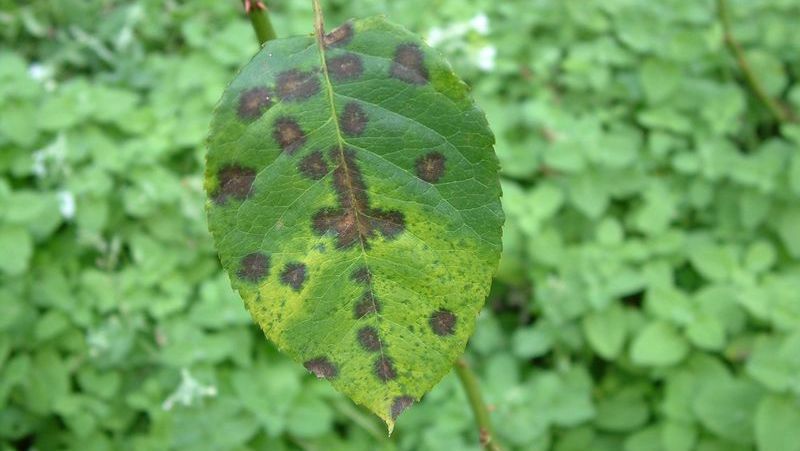
Black spot disease - brown spots on leaves
Brown spot and black spot on leaves are common diseases that affect a wide range of crops, from fruit trees such as oranges, tangerines, grapefruits, to vegetables such as tomatoes, peppers, and even ornamental plants. These diseases are often caused by fungi or bacteria, leading to the phenomenon of leaves being mottled, drying out, affecting the photosynthesis process, weakening the plant, reducing productivity and product quality. In this article, we will learn about the causes, symptoms, effects, and prevention measures of brown spot and black spot on leaves.
1. Causes of brown spot and black spot on leaves
Brown spot and black spot on leaves are mainly caused by fungi and bacteria. Some common types include:
- Pathogenic fungi: Fungi such as Alternaria spp., Cercospora spp., Phyllosticta spp., Mycosphaerella spp., and Colletotrichum spp. is a common agent causing brown spot and black spot on leaves in many crops. The fungus thrives in humid, high temperature conditions and is easily spread by wind, rain and irrigation water.
- Pathogenic bacteria: Some types of bacteria such as Xanthomonas campestris and Pseudomonas syringae can also cause leaf spot, creating brown or black spots. Bacteria are often spread through irrigation water, working tools and sucking insects.
- Weather and environmental conditions: Brown spot and black spot often develop strongly in humid, rainy and warm temperature conditions. Poorly drained soil or prolonged high humidity also create favorable conditions for fungi and pathogenic bacteria to develop.
2. Symptoms of brown spot and black spot on leaves

Symptoms of brown spot and black spot are quite easy to recognize with characteristic signs on the leaves. These symptoms may appear differently depending on the type of crop and the pathogen.
2.1. Symptoms on leaves
- Brown or black spots: Small brown or black spots appear on the leaves. Initially, the spots may appear in a small area on the leaf, then spread and merge into larger patches. For some plants, the spots may have a yellow halo around them.
- Dry and falling leaves: Diseased leaves often dry out from the edge of the leaf or from the spot, turn yellow or brown and may fall off early, affecting the plant's ability to photosynthesize and grow.
- Lá bị biến dạng: Deformed leaves: In some plants, large spots can cause leaves to become crooked, deformed and reduced in size.
2.2. Symptoms on the stem and fruit
- Spots on the stem and branches: In addition to the leaves, fungi and pathogenic bacteria can attack the branches and trunk, creating brown or black spots. Diseased branches will be weak, brittle and may gradually dry out.
- Fruit spots: For fruit trees, spot disease can spread to the fruit, forming brown or black spots that reduce product quality. Diseased fruit often does not develop normally, falls easily and loses commercial value.
3. Harmful effects of brown spots and black spots on leaves
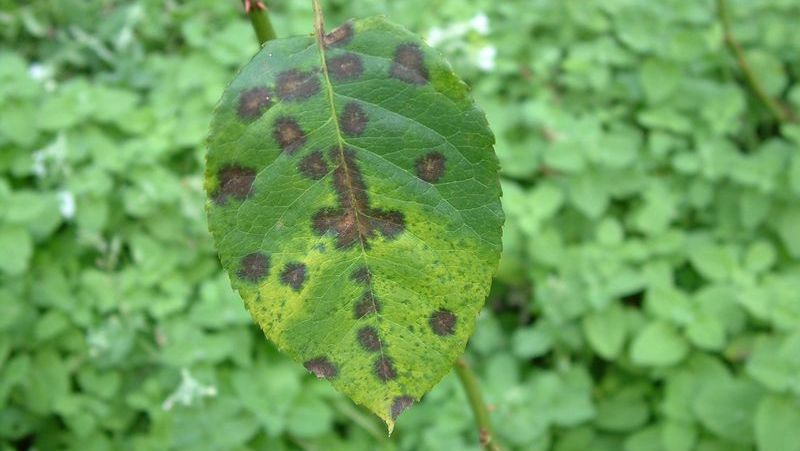

Brown spots and black spots cause many harmful effects on crops, especially fruit trees and vegetables. Some of the main harmful effects include:
- Reduced yield and quality: Brown spots and black spots reduce the photosynthetic capacity of leaves, causing the tree to weaken and grow slowly, thereby reducing the yield and quality of agricultural products.
- Weaken and gradually die the tree: If the disease is not controlled, the tree can be severely weakened, with many branches and leaves falling off, leading to the death of the tree, especially seedlings or young trees.
- Loss of commercial value: For fruit trees and vegetables, leaf and fruit spots reduce the commercial value, affecting the income of growers.
4. Conditions for disease occurrence
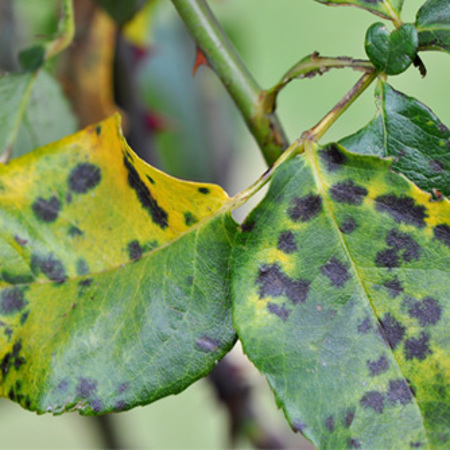

Brown spot and black spot diseases often occur and spread strongly in the following conditions:
- Wet weather, heavy rain: High humidity and warm temperatures are ideal conditions for fungi and bacteria to grow. Heavy rain and stagnant water on leaves create conditions for the disease to develop rapidly.
- Poorly drained soil: Waterlogged or poorly drained soil makes plants weaker and more susceptible to disease.
- High-density planting: Plants planted at too high a density reduce ventilation, increase local humidity, creating favorable conditions for the disease to spread.
5. Measures to prevent and control brown spot and black spot diseases on leaves

To prevent and control brown spot and black spot diseases on leaves, it is necessary to apply comprehensive management measures, from selecting disease-resistant varieties, improving environmental conditions, to using pesticides.
5.1. Water management and environmental conditions
- Water properly: Avoid over-watering and water in the morning to give the plants time to dry before dark. Avoid watering the leaves in the evening to reduce the risk of water remaining on the leaves overnight.
- Improve soil drainage: Ensure the garden has a good drainage system, especially during the rainy season, to avoid waterlogging which increases the risk of disease.
5.2. Pruning and garden sanitation
- Regular pruning: Prune infected branches and leaves and destroy them to prevent the source of infection. Pruning also helps the garden to be airy, reduces humidity and limits the growth of fungi and bacteria.
- Garden sanitation: Clean up diseased plant residues in the garden after each harvest. Diseased residues can be a place to store pathogens and spread to plants in the next crop.
5.3. Proper fertilization
- Balanced fertilization: Fertilizing with adequate and balanced nutrients helps plants to be healthy and increase their resistance to disease. In particular, fertilizers with high potassium and calcium content can help increase leaf durability and limit the spread of disease.
- Use organic fertilizers: Applying decomposed organic fertilizers or microbial fertilizers helps improve soil quality, enhance beneficial microorganisms and help plants grow sustainably.
5.4. Use of pesticides
- Preventive spraying: When the weather is humid and rainy, you can spray pesticides such as Mancozeb, Copper oxychloride, or Chlorothalonil to prevent the growth of fungi. Some drugs contain effective active ingredients such as: An-k-zeb 800WP, Byphan 800WP, Gone Super 350EC, Bretil Super 300EC, Scortlan 80WP, Thalonil
- Use of fungicides and bacteria: When a diseased plant is detected, it is necessary to spray fungicides or bacteria to control the disease. It is necessary to follow the dosage and usage to ensure safety and effectiveness.
5.5. Biological measures
- Use of biological products: Biological products containing beneficial microorganisms such as Trichoderma can be used to inhibit the growth of fungi and bacteria that cause disease.
5.6. Choose disease-resistant varieties
- Choose disease-resistant varieties: For some plants, you can choose varieties that are resistant to leaf spot or less affected by the disease. Using disease-resistant varieties helps reduce the risk of infection from the beginning.
6. Conclusion
Brown and black leaf spots are common diseases that cause a lot of damage to crops. However, with an understanding of the causes, symptoms and preventive measures, growers can control and minimize the damage caused by the disease.
Applying reasonable farming methods, adequate fertilization, regular pruning and garden cleaning, combined with the correct use of pesticides will help crops grow healthily, increase disease resistance and bring high yields.
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



