Active ingredient Glufosinate ammonium
Below is detailed information about the active ingredient Glufosinate ammonium—one of the most common herbicides on the market today, belonging to the chemical group of phosphinic acid derivatives. This active ingredient is often used as a non-selective herbicide in various forms of agricultural cultivation.

1. Overview of Glufosinate Ammonium
- Chemical name (IUPAC): Ammonium (RS)-2-amino-4-(hydroxy(methyl)phosphoryl)butyrate
- Molecular formula: C_5H_15N_2O4P
- Chemical group: Phosphinic acid derivative
Glufosinate ammonium is also abbreviated as GLA or GLUF on some product labels.

2. Mechanism of Action
Glufosinate ammonium is an inhibitor of the enzyme glutamine synthetase in plant cells. In simple terms:
- Inhibition of glutamine synthesis:
- When the enzyme glutamine synthetase is inhibited, the plant cannot synthesize glutamine from glutamate and ammonia.
- Accumulation of ammonia (NH3/NH4+):
- The level of ammonia in the cells increases to toxic levels, causing damage to the photosynthetic system (chloroplasts) and disrupting metabolic processes.
- Causing plant tissue death:
- Leaf tissue undergoes necrosis, causing the plant to wilt and die within a few days to a week, depending on the type of grass and environmental conditions.
This mechanism is different from glyphosate (which inhibits the EPSPS enzyme) and also different from paraquat (which causes cell destruction through oxidation), so glufosinate ammonium is often used alternately or as a substitute in cases of glyphosate-resistant weeds.

3. Characteristics and Advantages
- Non-selective herbicides:
- Effective against many types of broadleaf and grass weeds.
- Suitable for cleaning weeds before planting or for treating perennial weeds in industrial crops and fruit trees.
- Contact herbicides with limited translocation:
- Primarily act at the point of contact on the leaves, but have a certain degree of systemic absorption, spreading slightly within the plant.
- Require good coverage when sprayed to achieve maximum effectiveness.
- Relatively fast efficacy:
- Leaf burn symptoms may appear after 2–5 days, and weeds die completely within about 7–14 days (depending on conditions).
- Low long-term residue in soil:
- Glufosinate ammonium is relatively quickly degraded by microorganisms, typically having a half-life (DT50) of 3–20 days, depending on temperature, moisture, and soil type.
- Reduced risk of resistance:
- Alternating Glufosinate ammonium with other active ingredients (e.g., glyphosate group, PPO inhibitors, ALS inhibitors, etc.) helps reduce the risk of weeds developing single-resistance mechanisms.

4. Dosage and administration
- Common dosage:
Typically, Glufosinate ammonium is recommended for use at a concentration ranging from 0.6 to 1.5 kg of active ingredient per hectare (depending on the type of grass and the level of infestation). - Timing of application:
- Apply when the grass is still young (2–5 leaves) or during the vigorous growth stage of the grass.
- It is advisable to spray when the weather is dry, with little wind, and to avoid rain for 4–6 hours after application.
- Method:
- Use a pressure sprayer, a nozzle with a shield (if protection of the main crops is needed), or mechanization with a sprayer or drone.
- It is recommended to control the grass before it becomes too old and tough, as effectiveness will decrease if the grass has developed a large root system or is flowering.

5. Toxicity and safety of use
- Acute toxicity (LD50 oral, rats):
- Approximately 2000 mg/kg body weight, classified as low to moderate toxicity compared to many other pesticides.
- Environmental impact:
- Due to its rapid degradation in the environment, Glufosinate ammonium is considered to have low long-term accumulation.
- However, it is still necessary to prevent the pesticide from spreading into natural water sources, affecting aquatic organisms.
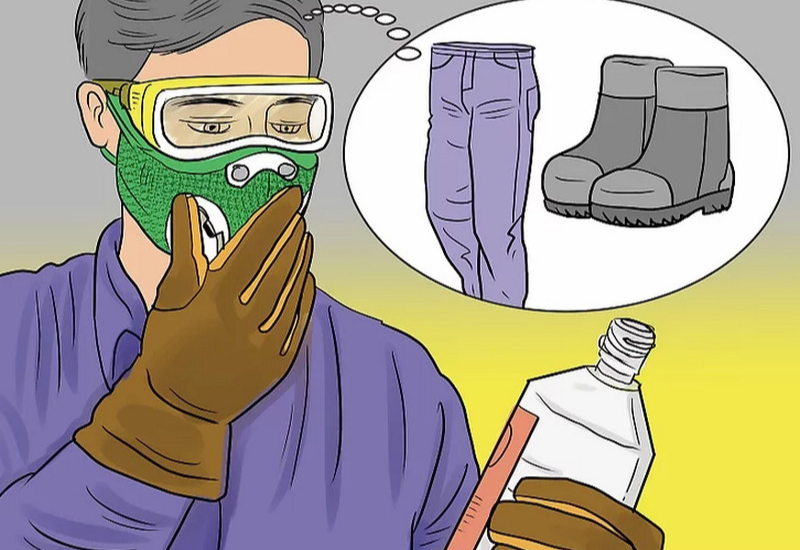
- Protective measures:
- Wear gloves, a mask, and safety goggles to avoid inhaling pesticide mist or skin contact.
- Clean the spray equipment and wash hands and feet after use, and store the pesticide in a safe place, out of reach of children and pets.
- Pre-harvest interval:
- Generally not applicable to food crops if sprayed directly (as it is a non-selective herbicide), but only used for weed control before or between rows of perennial plants.
- In the case of spraying around the base of fruit trees, check the product label to comply with the pre-harvest interval (if any) before harvesting.

6. Notes and recommendations
- Do not let the herbicide come into contact with the main crops if they do not have the Glufosinate-resistant gene (or are not protected). Glufosinate ammonium can cause leaf burn, affecting yield
- Rotate active ingredients: To avoid the development of herbicide-resistant weeds, it is advisable to combine or alternate with other active ingredients that have different mechanisms (glyphosate, atrazine, quazifop, etc.).
- Be cautious during the flowering stage: If there are flowering plants around the field, avoid spraying when pollinating insects (bees, butterflies) are actively foraging to minimize impact.
- Refer to the manufacturer's instructions: Each company providing Glufosinate ammonium may have different active ingredient concentrations and excipient formulations, so it is important to follow the recommended dosage, mixing ratios, and spraying times as indicated on the label.

7. Prospects and applications in agriculture
- Replacing glyphosate in some areas: In the context of many countries tightening regulations on glyphosate due to health and environmental concerns, Glufosinate ammonium has become an important alternative for non-selective herbicide purposes
- Genetically modified organisms (GMO): In some countries, crops resistant to Glufosinate (similar to glyphosate-resistant crops) are being developed to help farmers spray herbicides without harming the main crops.
- Reducing pest pressure and labor costs: The proper use of Glufosinate ammonium helps save labor for manual weeding, effectively controls weeds, and improves the farming environment.

Conclusion
Glufosinate ammonium is a non-selective herbicide that inhibits the enzyme glutamine synthetase, effectively controlling many species of weeds. Its advantages include relatively fast efficacy and low long-term residues in the environment, and it can be used as a substitute for glyphosate in some cases to avoid resistance. However, to use it safely and effectively, farmers need to adhere to the correct dosage, spraying methods, and combine it with sustainable farming practices to protect health, the environment, and maintain long-term weed control effectiveness.
Here are some products containing the active ingredient Glufosinate ammonium: Khai hoang Q7, Khai hoang Q10, Trau rung den, Newfosinate 150SL, Kenbast 15SL, Shina 18SL, Gussi Bastar 200SL, Gussi Bastar 200SL (Weed killer song), Co Chay Hong Ha Nhi, Than Lua 300, Lac Da, Voi Rung,…
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



