
Integrated Weed Management (IPM): A Comprehensive and Sustainable Solution for Agriculture
Learn how to apply IPM – an Integrated Pest Management approach – that helps farmers control weeds effectively, reduce dependence on chemical herbicides, protect the environment, and increase crop productivity.
1. What Is IPM (Integrated Pest Management)?
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach that combines multiple strategies including biological, chemical, mechanical, manual, and cultural practices to:
- Achieve long-term, effective weed control
- Reduce dependency on chemical herbicides
- Prevent the development of herbicide-resistant weeds
- Protect the environment and the agricultural ecosystem
2. Why Apply IPM in Weed Management?

In practice, relying on a single method – especially chemical herbicides – often leads to:
- Herbicide-resistant weeds that quickly regrow
- Negative impacts on soil, water, and air quality
- Imbalanced agricultural ecosystems
- Reduced long-term effectiveness and increased production costs
By applying IPM, farmers can tackle these issues at the root by diversifying weed control tools, gradually weakening and eliminating weeds’ ability to regenerate.
3. Key Components of IPM in Weed Management
3.1. Cultural Practices
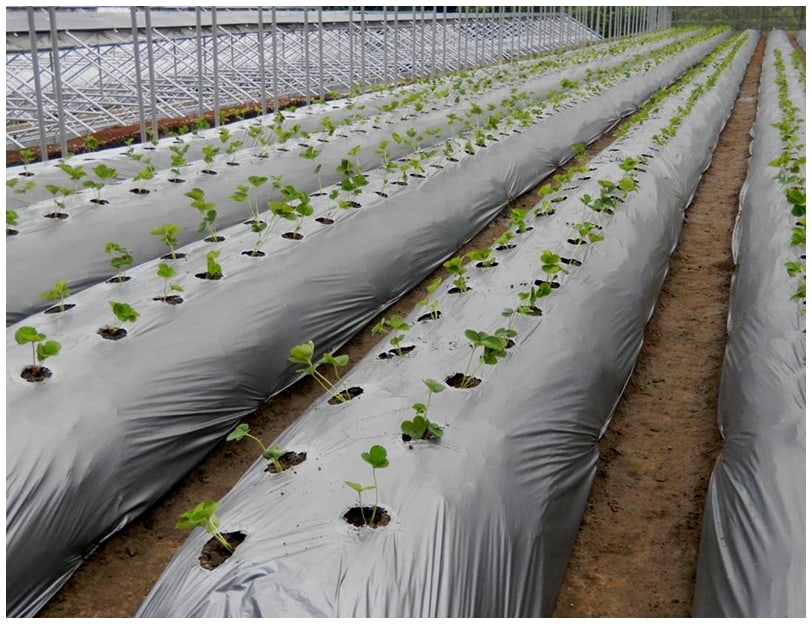

- Crop rotation: Disrupts weed life cycles
- Intercropping: Provides shading to suppress weed growth
- Mulching with straw, compost, or plastic film: Prevents weed emergence from the soil
3.2. Mechanical and Manual Methods
-500x333.jpg)
- Use of brush cutters, row weeders, hoes, hand tools
- Manual weeding around tree bases or in small nursery areas
3.3. Chemical Control

- Rotate different herbicide active ingredients
- Apply herbicides only when weed infestation exceeds economic thresholds
- Use selective or non-selective herbicides depending on the crop
3.4. Biological Control

- Employ pathogenic fungi, beneficial insects, or natural germination inhibitors
- Introduce beneficial microorganisms to reduce weeds’ competitiveness
4. Benefits of Applying IPM for Weed Control
|
Benefit |
Description |
|
Sustainable effectiveness |
Weeds are suppressed from multiple angles, making recovery difficult |
|
Environmental protection |
Reduces chemical residues in soil and water |
|
Resistance management |
Herbicide rotation prevents weed resistance |
|
Cost efficiency over time |
Initial costs may be higher but offer long-term savings |
|
Adaptability |
Flexible for different regions, seasons, and crops |
5. Practical Examples of IPM Application
In rice fields:
- Rotate rice with other crops
- Use row seeding instead of broadcast seeding
- Combine pre-emergent herbicides with mechanical weeding between rows
- Avoid repeated use of the same herbicide
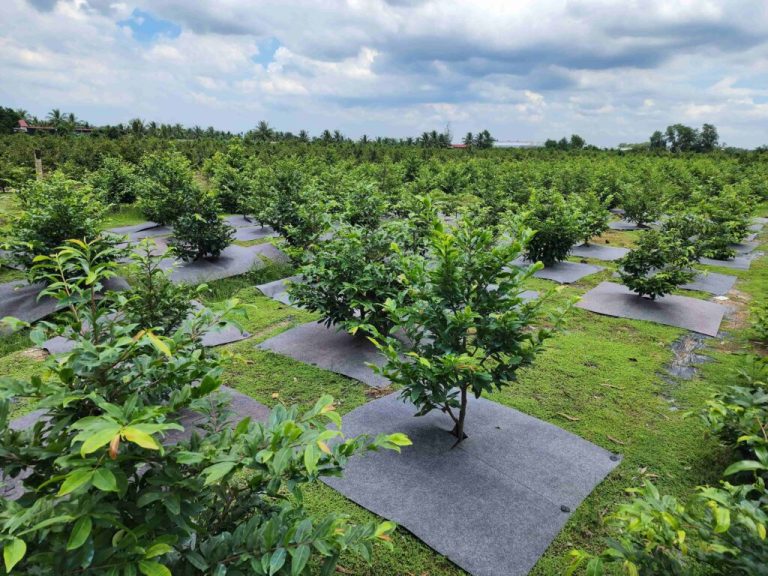

In perennial crops like coffee, pepper, and rubber:
- Mulch tree bases with straw, rice husk, or agricultural film
- Use Glufosinate Ammonium as a contact herbicide
- Apply brush cutting machines periodically
- Intercrop with legumes like peanuts or green beans to suppress weeds
6. Steps to Implement IPM for Weed Control
- Field assessment: Identify weed species, density, and damage level
- Plan integrated strategies: Select suitable methods based on crop type and season
- Execute comprehensively: Apply mechanical, chemical, and biological methods correctly
- Monitor and evaluate: Track effectiveness and adjust strategies as needed
- Rotate techniques and herbicides: Avoid dependence on any single method
7. Notes for Large-Scale IPM Implementation
- Ensure cooperation among farmers within the same area
- Provide basic IPM training for farmers
- Collaborate with plant protection centers and agricultural extension stations for monitoring and guidance
- Maintain weed data records for long-term planning
8. Conclusion
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is not just a technical solution—it is a strategic direction toward smart, sustainable, and environmentally friendly agriculture. Amid climate change, rising herbicide resistance, and increasing food safety demands, adopting IPM for weed control is a necessary trend for responsible and progressive farming.
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



