Effective Herbicide Rotation: The Key to Preventing Resistance and Keeping Your Orchard Weed-Free
Learn how to rotate herbicide actives and combine Glufosinate with pre- and post-emergent herbicides to eliminate weeds, prevent resistance, and maintain long-term weed control in fruit orchards.
Table of Contents
- Why Rotate Herbicide Actives?
- Glufosinate – Strengths and Limitations
- Understanding Pre- vs Post-Emergent Herbicides
- How to Combine Glufosinate with Other Herbicide Groups
- Suggested Annual Rotation Plan
- Conclusion
1. Why Rotate Herbicide Actives?

Just like pests can develop resistance to insecticides, weeds can develop resistance to herbicides, especially if:
- The same active ingredient is used repeatedly over multiple seasons
- Improper dosage is applied → partial weed kill
- Weeds regrow quickly from underground stems or tubers
🔁 Rotating herbicides helps to:
✅ Lower resistance risk
✅ Target different weed species
✅ Extend herbicide effectiveness
✅ Reduce long-term weed control costs
2. Glufosinate – Strengths and Limitations

Glufosinate is a non-selective post-emergent contact herbicide that kills weeds where sprayed.
Strengths:
- Fast-acting weed burn-down
- Does not translocate to roots → safer for fruit trees
- Works well in orchards when sprayed close to the base
- Low resistance risk if applied correctly
⚠️ Limitations:
- Ineffective against germinating weed seeds
- Weeds can regrow if no pre-emergent is used
3. Understanding Pre- vs Post-Emergent Herbicides

|
Herbicide Type |
Timing of Use |
Mode of Action |
Example Actives |
|
Pre-emergent |
Before weed germination |
Inhibits weed seed development |
Pendimethalin, Butachlor |
|
Post-emergent |
After weed emergence |
Kills existing weeds |
Glufosinate, Glyphosate |
📌 Combining both provides:
→ Prevention of new weed growth from seeds
→ Elimination of existing weeds → total field cleanliness
4. How to Combine Glufosinate with Other Herbicide Groups

✅ Combo 1 – Prevention + Elimination
- Early season (after soil prep):
→ Apply Pendimethalin to block seed germination - Mid-season (when weeds appear):
→ Apply Glufosinate to kill both broadleaf and grassy weeds
✅ Combo 2 – Rotational Approach
|
Season |
Recommended Strategy |
|
Season 1 |
Glufosinate (post-emergent only) |
|
Season 2 |
Switch to Butachlor (pre-emergent) |
|
Season 3 |
Rotate back to Glufosinate or Glyphosate |
📌 Note:
- Avoid using Glufosinate for more than 2 consecutive seasons
- Rotate at least two different chemical groups to prevent resistance
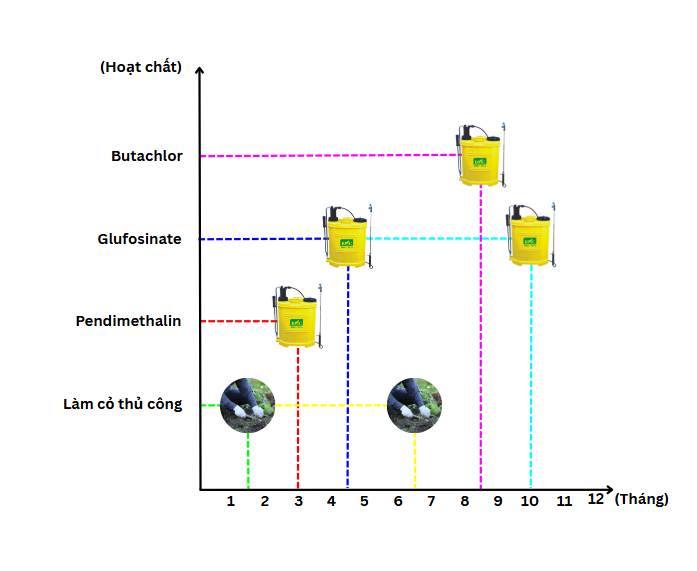
5. Suggested Annual Weed Control Schedule (for Orchards)
|
Month |
Recommended Actions |
|
January–February |
Manual weeding – herbicide break to avoid early-season residue |
|
March |
Apply Pendimethalin before first rain |
|
April–May |
Apply Glufosinate when young weeds emerge |
|
June–July |
Combine manual weeding and minimal spraying |
|
August–September |
Apply Butachlor after heavy rains |
|
October |
Apply Glufosinate as pre-harvest clean-up |
6. Conclusion
Rotating and combining herbicide active ingredients is the key to long-term weed management. It helps prevent resistance, protects your crops, and saves money in the long run.
👉 Glufosinate Ammonium is an ideal herbicide when combined correctly with pre-emergents like Pendimethalin or Butachlor, creating a “double shield” to stop both new and existing weeds.
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



