
Cartap Hydrochloride: A Priority Solution for Organic Farming and GAP Standards?
As consumers increasingly focus on clean and safe food, organic agriculture and GAP (Good Agricultural Practices) are emerging as sustainable development trends. A common question among farmers and agribusinesses is: Is Cartap Hydrochloride suitable for organic farming or models such as VietGAP and GlobalGAP? Let’s examine this in detail.
1. Overview of Cartap Hydrochloride
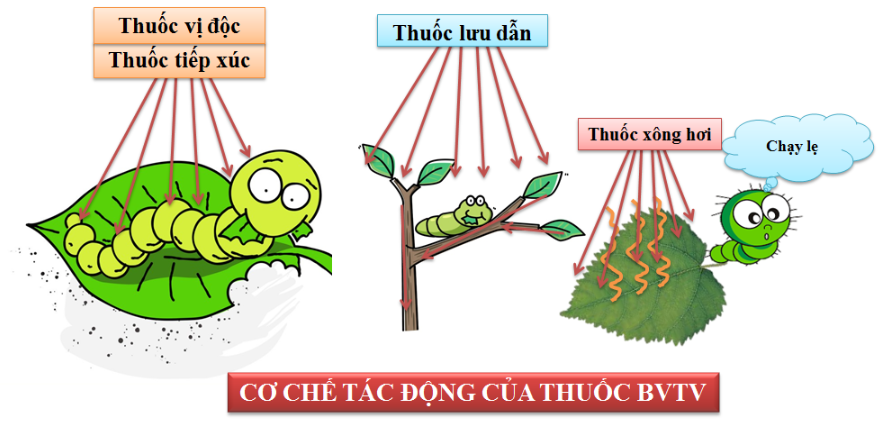
Cartap Hydrochloride is an insecticidal active ingredient from the Nereistoxin analogue group. It acts on pests’ nervous systems through contact and ingestion toxicity. It is commonly used to control leaf rollers, stem borers, and diamondback moths, especially in rice, vegetables, tea, corn, and fruit trees.
Key advantages:
- Low toxicity to humans and warm-blooded animals.
- Rapid biodegradation with minimal residue.
- Does not trigger red spider mite outbreaks like some pyrethroids.
2. Is Cartap Hydrochloride Suitable for Organic Farming?

Answer: NO – Not fully.
Cartap is not classified as a biological pesticide and lacks OMRI certification (Organic Materials Review Institute), so it is not allowed in organic farming under international standards.
Why?
- It is a synthetic compound, not derived from natural sources like Spinosad or Abamectin (which originate from microbes).
- Organic certifiers (e.g., USDA Organic, EU Organic) exclude Cartap from the list of permitted crop protection substances.
However, if you're practicing low-input or semi-organic methods, Cartap may be considered in early crop stages or during pest outbreaks—provided a sufficient pre-harvest interval (PHI) is observed to avoid residues.
3. Is Cartap Allowed in GAP Systems (e.g., VietGAP, GlobalGAP)?


Answer: YES – With conditions:
- Must be used according to proper dosage and PHI, with clear application records.
- Must comply with the list of approved pesticides by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (Vietnam).
- Must adhere to food safety and environmental protection guidelines during application.
Advantages of using Cartap in GAP models:
- Low resistance development; can be rotated effectively with other actives like Emamectin or Indoxacarb.
- Fast degradation, helping to reduce risk of exceeding MRLs (Maximum Residue Limits).
- Does not cause leaf burn and has minimal impact on beneficial soil microbes.
4. Comparison with Other Clean Agriculture Pesticides
|
Active Ingredient |
Origin |
Organic Approved |
GAP Approved |
Notes |
|
Cartap |
Synthetic |
❌ |
✅ |
Follow PHI and dosage strictly |
|
Spinosad |
Microbial (Streptomyces) |
✅ |
✅ |
Very safe, higher cost |
|
Abamectin |
Microbial |
✅ |
✅ |
Sensitive to sunlight; spray in late afternoon |
|
Neem oil |
Botanical |
✅ |
✅ |
Less effective on mature pests |
|
Emamectin Benzoate |
Semi-synthetic |
❌ |
✅ |
Best used in rotation to manage resistance |
5. Recommendations for Using Cartap in Clean Farming Models

- Do not use Cartap in farming under certified organic (e.g., USDA Organic) standards.
- It can be used under VietGAP/GlobalGAP, with:
- Detailed application records.
- 7–14 days pre-harvest interval.
- Rotation with biological or botanical pesticides like Spinosad or Neem oil.
- Preferably use at the early crop stages or when pests are still young for better control and fewer applications.
6. Conclusion
While Cartap Hydrochloride is not an organic pesticide, it remains an optimal solution for GAP-compliant farming thanks to its high efficacy, low toxicity, and rapid degradation. When used responsibly and in combination with biological alternatives, Cartap can contribute significantly to safe crop production and meeting export quality standards.
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



