
Common Harmful Fungi and Bacteria in Soil: Identification and Prevention
A comprehensive guide to harmful fungi and bacteria commonly found in agricultural soils, such as Fusarium, Phytophthora, Ralstonia, and more. Learn how to identify symptoms, affected crops, and effective prevention methods to protect your harvest.
Table of Contents
- Why It’s Important to Care About Soil-Borne Fungi and Bacteria
- Common Soil-Borne Fungal Pathogens
- Common Soil-Borne Bacterial Pathogens
- Crops Most Susceptible to Soil-Borne Diseases
- Effective Methods for Treatment and Prevention
- Conclusion
1. Why It’s Important to Care About Soil-Borne Fungi and Bacteria

Soil pathogens are "silent killers" that harm crops from the roots up, leading to:
- Stunted growth, wilting, and yellowing with no clear cause
- Root rot, bacterial wilt, basal stem rot
- Persistent disease cycles across seasons if untreated
➡️ Preventing soil diseases means preventing from the root, reducing damage across the entire crop cycle.
2. Common Soil-Borne Fungal Pathogens
1. Fusarium spp.
- Diseases: Fusarium wilt, root rot
- Affected crops: Chili, tomato, watermelon, cucumber, banana, pepper
- Symptoms: Yellowing from the bottom up, midday wilting, brown roots, blocked vascular tissue
2. Rhizoctonia solani

- Diseases: Damping-off, basal stem rot
- Affected crops: Vegetables, rice, flowers
- Symptoms: Dark brown rot at the base, seedling collapse
3. Pythium spp.

- Diseases: Root rot, seedling death
- Features: Thrives in wet soil conditions
- Affected crops: Melon, mustard greens, onion, chrysanthemum
4. Phytophthora spp.

- Diseases: Stem rot, fruit rot, leaf blight
- Affected crops: Durian, pepper, mango, tomato, chili
- Notable: Highly aggressive and spreads rapidly after rain
3. Common Soil-Borne Bacterial Pathogens
1. Ralstonia solanacearum

- Disease: Bacterial wilt
- Affected crops: Tomato, chili, potato, banana
- Symptoms: Whole plant wilts, soft stem, milky white ooze when stem is cut
2. Agrobacterium tumefaciens

- Disease: Crown gall
- Affected crops: Longan, lychee, rose, guava
- Symptoms: Rough, tumor-like galls on roots or base; weak plant growth
3. Erwinia spp.
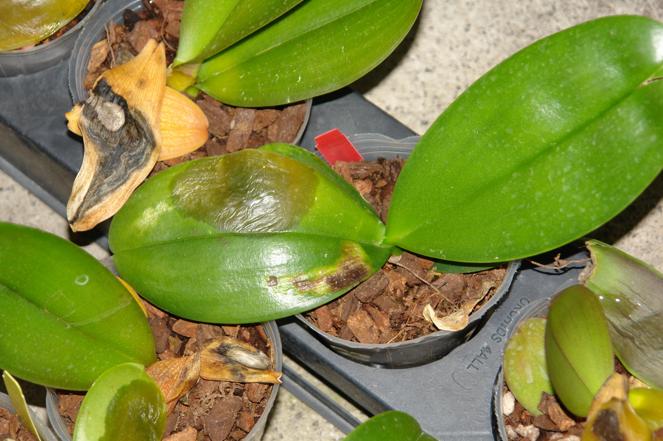

- Diseases: Soft rot, root decay
- Affected crops: Bulbs and tubers (e.g., watermelon, garlic, onion)
- Symptoms: Mushy, foul-smelling rot
4. Crops Most Susceptible to Soil-Borne Diseases

|
Crop Type |
Common Diseases |
|
Tomato, chili, eggplant |
Bacterial wilt, Fusarium, Rhizoctonia |
|
Watermelon, melon |
Root rot, Pythium, Phytophthora |
|
Fruit trees (durian, mango, guava) |
Stem rot, anthracnose, bacterial gall |
|
Short-cycle vegetables |
Damping-off, seedling death |
|
Rice |
Root blast, yellow dwarf, grain discoloration |
5. Effective Methods for Treatment and Prevention
✅ 1. Sun-dry soil between planting cycles
➡️ Interrupts the life cycle of soil pathogens
✅ 2. Rotate with crops from different families
➡️ Reduces pathogen buildup specific to certain crops
✅ 3. Apply lime, well-composted organic fertilizer, and Trichoderma
➡️ Boosts soil immunity, suppresses pathogens
✅ 4. Use biological control agents (antagonistic fungi)
➡️ Such as Trichoderma, Bacillus subtilis, etc.
✅ 5. Avoid using raw manure or contaminated water
➡️ Prevents introduction of new pathogens
✅ 6. Limit prolonged chemical fungicide and bactericide use
➡️ Protects beneficial microbial balance in the soil
6. Conclusion
Harmful fungi and bacteria in soil are leading causes of stunted growth, wilting, and crop failure. Understanding these pathogens, how they spread, and how to treat them is the key to protecting your crops effectively.
👉 Proactive soil care — through remediation, beneficial microbes, and proper crop rotation — ensures sustainable farming and long-term productivity.
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



