
Mode of Action of Propiconazole: How Does It Kill Fungi?
Propiconazole is one of the most widely used active ingredients in fungicides today, especially effective against diseases such as rice blast, rust, powdery mildew, leaf spots, anthracnose, and more. However, not everyone understands how Propiconazole works, why it is so effective, and why it's widely used in many crop protection products.
Let’s dive into the detailed mechanism of action of Propiconazole in the article below.
1. Overview of Propiconazole
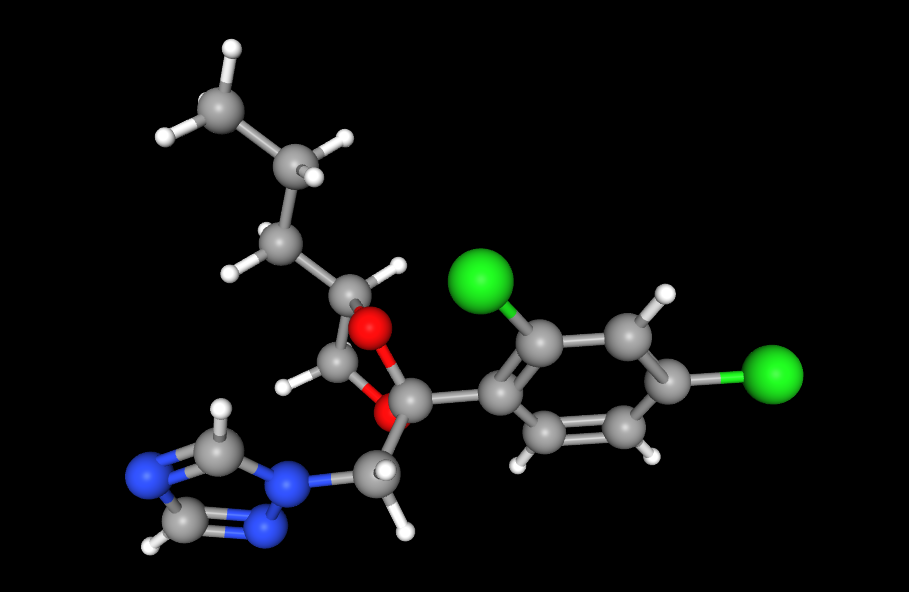
- Chemical name:
1-[[2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-propyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-yl]methyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole - Chemical group:
Triazole (a subgroup of azole fungicides) - Physical form:
Pale yellow liquid, highly soluble in organic solvents - Key features:
Systemic fungicide, broad-spectrum, effective in both prevention and treatment
Propiconazole is a strongly systemic fungicide, meaning it penetrates plant tissues and is translocated to various parts of the plant, offering whole-plant protection—not just surface-level.
2. Mode of Action of Propiconazole

🧬 Inhibits Ergosterol Biosynthesis – the “Weak Heart” of Fungal Cells
Fungal cells have a protective outer membrane, much like a “shield,” which helps them grow and survive. This membrane is primarily composed of ergosterol, which functions similarly to cholesterol in animal cells.
Propiconazole belongs to the triazole group and inhibits the C14-demethylase enzyme—a critical enzyme in the synthesis of ergosterol. When this enzyme is blocked:
- The fungal cell membrane fails to form properly
- Metabolic processes become disordered
- Fungi can’t grow and eventually die
💡 In simple terms: Propiconazole starves fungal cells of what they need to build their membranes, slowly killing them from the inside.
3. Systemic and Translocation Properties

Once applied to the plant, Propiconazole:
- Penetrates through leaves, stems, or roots
- Moves within the plant’s vascular system (mainly upward)
- Kills fungi hidden inside plant tissues—even before symptoms appear
This gives Propiconazole a major advantage over contact fungicides, which only kill fungi on the leaf surface.
4. What Types of Fungi Does It Kill?
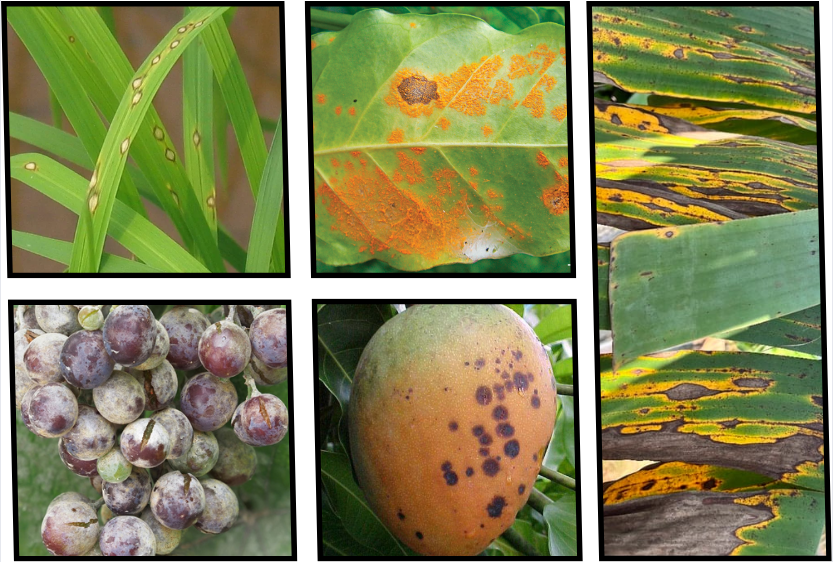

Propiconazole is highly effective against various plant pathogenic fungi, including:
|
Fungal Species |
Common Disease |
|
Pyricularia oryzae |
Rice blast (on rice) |
|
Puccinia spp. |
Rust (on beans, coffee, etc.) |
|
Oidium spp. |
Powdery mildew (on grapes, melons, mango) |
|
Colletotrichum spp. |
Anthracnose (on chili, mango, fruit trees) |
|
Cercospora spp. |
Leaf spot, leaf scorch |
5. Advantages Compared to Other Active Ingredients
|
Criteria |
Propiconazole |
Mancozeb (Contact) |
Metalaxyl (Other Systemic) |
|
Mode of action |
Systemic |
Contact |
Systemic |
|
Translocation |
Strong, upward movement |
None |
Present |
|
Spectrum of activity |
Broad |
Medium |
Narrower |
|
Preventive & curative |
Yes (early-stage curative) |
Mainly preventive |
Mainly preventive |
|
Risk of resistance |
Yes (if overused) |
Lower |
Yes |
✅ Conclusion: Propiconazole is a powerful choice when fast, comprehensive, and early-stage fungal control is needed.
6. Usage Guidelines
- Do not use more than 2–3 times per crop season to avoid resistance.
- Rotate with other chemical groups (e.g., Mancozeb, Azoxystrobin, Chlorothalonil).
- Spray early at the first signs of disease—don’t wait until the outbreak spreads.
- Avoid mixing with highly alkaline products to prevent active ingredient degradation.
7. Conclusion
Propiconazole is a potent systemic fungicide that inhibits ergosterol biosynthesis, damaging fungal cells and causing their gradual death. With strong translocation ability and a broad spectrum of action, it is a crucial tool in managing fungal diseases in crops.
👉 To get the best results and prolong its effectiveness, farmers should use it at the right dosage, right time, and rotate wisely with other fungicides.
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



