
Which Crops Are Most Suitable for CS Pesticides?
Capsule Suspension (CS) pesticides are an advanced technology in crop protection, offering many advantages such as slow release, extended effectiveness, strong adhesion, and crop safety. However, not all crops actually require CS formulations.
So, which crops should prioritize CS, and when should farmers choose CS over traditional pesticides? Let’s break it down.
✅ 1. Long-Term Industrial Crops – Highly Suitable for CS
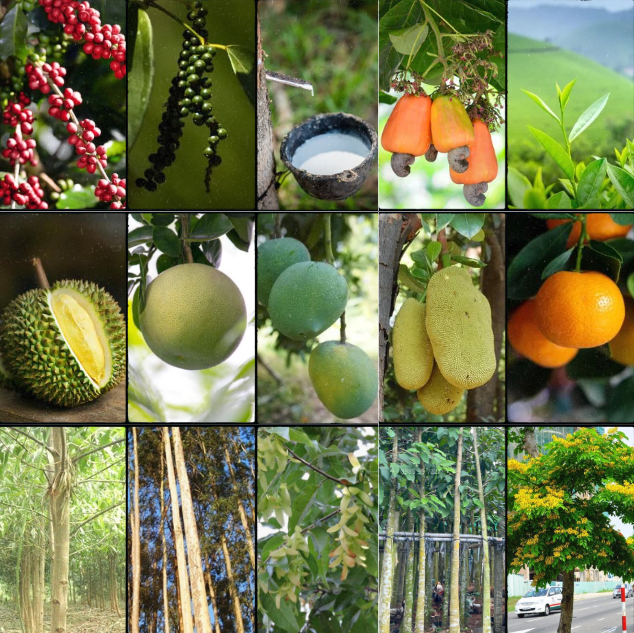

Crops with long growth cycles and fewer spray intervals are ideal for CS pesticides because:
- Reduce the need for frequent spraying
- Extended effect saves labor costs
- Lower residue risks due to gradual release of active ingredients
Examples:
|
Crop Group |
Specific Examples |
|
Long-term industrial crops |
Coffee, pepper, rubber, cashew, tea |
|
Perennial fruit trees |
Durian, pomelo, mango, jackfruit, orange, star apple |
|
Timber/shade trees |
Acacia, eucalyptus, mahogany, dipterocarp, blackwood |
💧 2. Crops in Rainy Regions – Should Prioritize CS
CS pesticides provide superior adhesion and rainfastness, making them especially useful in:
- Central Highlands, Southeast – unpredictable rainfall
- Mekong Delta – long rainy seasons, high humidity
- Orchards with limited access for frequent spraying
🌧️ During the rainy season, CS can maintain effectiveness for 10–120 days, greatly minimizing wash-off.
🍃 3. Sensitive Crops – CS Reduces Leaf Burn Risk

Some crops are highly sensitive to solvent-based pesticides (EC, ME), leading to leaf burn, yellowing, or fruit drop if overdosed. CS, with its slow-release system, avoids phytotoxic “shocks,” making it more suitable for:
- Durian, pomelo, sweet orange – prone to leaf burn
- Jackfruit, star apple, longan – susceptible to premature fruit drop with EC products
- Organic vegetables, cut flowers – require low residues and high safety
📦 4. Crops Under Organic or GAP-Oriented Cultivation
CS pesticides help:
- Reduce spray frequency → lower residues on produce
- Enhance effectiveness → less reliance on conventional chemicals
- Provide low odor and safer handling in peri-urban farming
👉 Farmers producing under VietGAP, GlobalGAP, or Organic standards, especially for export to Japan/Europe, are strongly advised to use certified CS products.
❌ Short-Term Crops – CS Not Necessary
For short-term crops, CS may not be cost-effective:
- Short life cycles → don’t need prolonged effect
- Higher cost → not economical for quick crops
Examples: mustard greens, water spinach, snap beans, short-term rice (90 days), seasonal flowers.
📌 Conclusion
|
Scenario |
Should Use CS? |
|
Long-term crops (industrial, fruit) |
✅ Yes |
|
Rainy season, hard-to-access fields |
✅ Highly suitable |
|
Sensitive crops (risk of leaf burn) |
✅ Recommended |
|
Organic/GAP, high safety required |
✅ Should use |
|
Short-term crops, low-cost priority |
❌ Not necessary |
Bình luận
Những bình luận mới nhất



